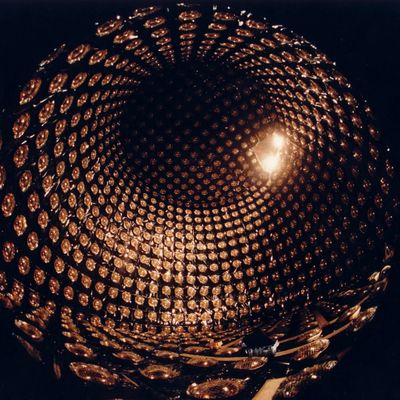
About the Experiment
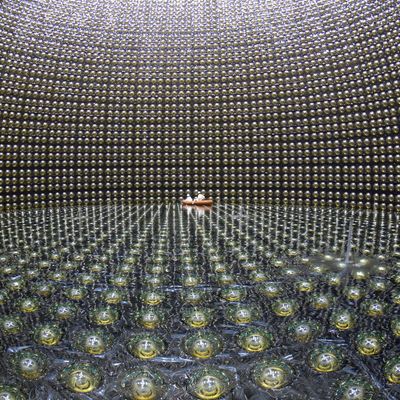
The Tokai-to-Kamioka (T2K) experiment is a long baseline neutrino oscillation experiment. A beam of muon neutrinos (or anti-neutrinos) is created at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) in Tokai. Beam properties are measured at a Near Detector complex, before the neutrinos travel 300 km towards the East of Japan. While travelling, the majority of muon neutrinos in the beam spontaneously change their flavour, and are then measured again at a Far Detector, located underneath Mount Ikeno near Kamioka. Studying the details of this behaviour, also known as flavour oscillation, is the subject of study for the T2K experiment. Hints were found that the probability for such an oscillation differs between neutrinos and anti-neutrinos oscillate, which - if confirmed - could provide an explanation for the difference in the amount of matter and antimatter in our observable universe. In order to correctly interpret the measurements at the Far Detector, characteristics of neutrino interactions with matter have to be understood in great detail, and also have to be correctly translated between Near- and Far Detector. This is the research focus of the CERN EP-NU group. Neutrino interactions at the Near Detector and the modelling thereof are researched, and performance studies for an upgrade of the ND280 Near Detector are conducted. In addition, hardware components for the detector upgrade are developed in close collaboration with other institutes and the CERN Neutrino Platform. See here for details on the ND280 upgrade.